Whether you are new to the world of WordPress websites or have been a part of this community for a while now, nothing must seem more frustrating than the occasional 400 Bad Request errors that won’t let your website load. That’s why, today, we will take a closer look into this common error, figure out its causes, and provide all troubleshooting steps possible.

When your WordPress website displays 400 Bad Request errors, it can be quite challenging to pinpoint the actual reason behind it. The cause might simply be the result of a file size exceeding the server limit, or it can be something more complex such as an unsynchronized DNS lookup cache.
Regardless, there are several tried and tested troubleshooting methods that can instantly help to solve this error without breaking a sweat. And to help you have the best experience creating and running your website, we will list out every solution we know. But before we get into the answers, let’s define what a 400 Bad Request error is and explore some of the likely causes.
What Do We Understand By A HTTP 400 Bad Request Error?
A 400 Bad Request error (also known as error 400 or HTTP error 400) is an HTTP status code and indicates that the request you issued to your web server has malfunctioned. In other words, the data stream that is sent to the web server when you request to view or use a web page is not processed due to an error.
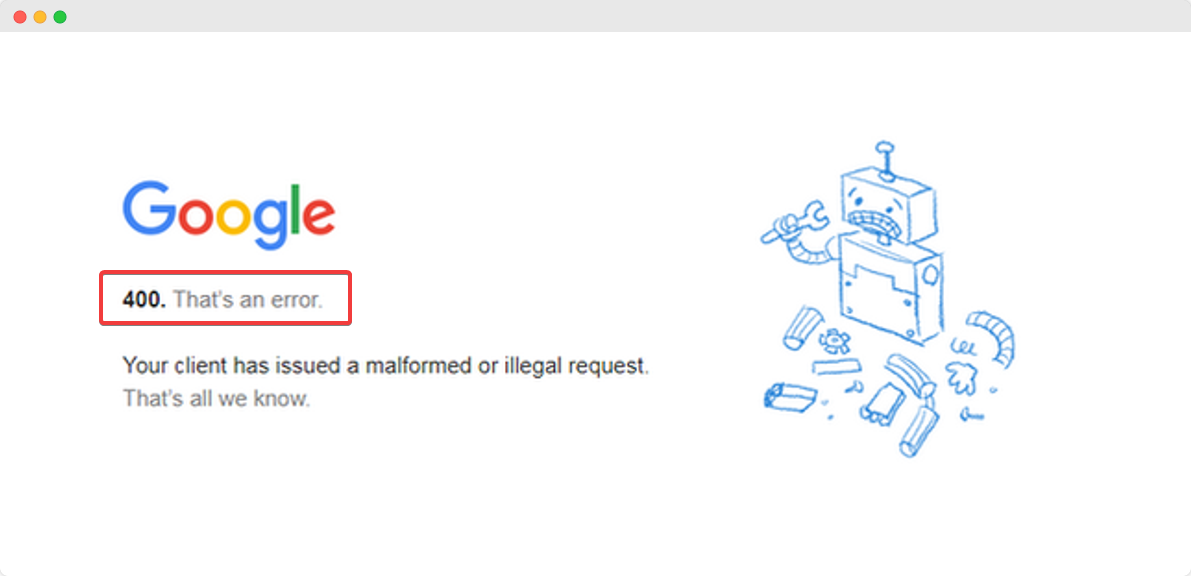
It is usually considered a generic client error, and it is returned when your web server does not understand the request and considers it to be an error on your part. The key concept to grasp here is that the 400 Bad Request error is related to your request that occurs even before the server even processes it.
It is one among a group of 28 HTTP 4xx errors known as client errors because they are usually caused by an issue caused by the browser or a local device, not the hosting server. Other errors of this family include:
⚠️ 402 Payment Required – The request cannot be processed until the user makes a payment. This is currently not in use.
⚠️ 403 Forbidden – The browser does not have permission to take that request or authorize it and forbids you from accessing the web page.
⚠️ 404 Not Found – The page you are looking for does not exist or cannot be found on the server. This is probably one of the most common errors on WordPress.
⚠️ 408 Request Timeout – The server did not receive or process the request made by the user on time
The Types Of 400 Bad Request Error Messages To Expect
Now that we understand what a 400 Bad Request error is, the next step is to get familiarized with what types of error messages you might receive from your server when this happens.
And to add to your frustration, this 400 Bad Request error text may come with multiple names and visualizations depending on the various web browsers, servers, and operating systems. However, they all point to the same error regardless of how it looks, and all browsers respond with a generic 400 status code.
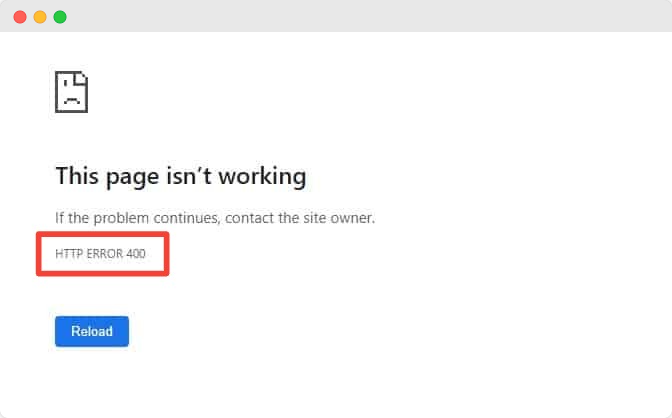
Website developers can also customize what the 400 Bad Request error page will look like on their website to keep users engaged even when their sites fail to load. Aside from such custom-made 400 error pages, most websites or browsers display the bad request error with the descriptions shown below:
- 400 Bad Request
- HTTP 400 Bad Request
- HTTP Status 400 – Bad Request
- 400 Bad Request Error
- HTTP Error 400
- Bad Request: Error 400
- HTTP Error 400 – Bad Request
- Bad Request. Your browser sent a request that this server could not understand.
- HTTP Error 400. The request hostname is invalid
- Bad Request – Invalid URL
Possible Common Causes Of A 400 Bad Request Error
So, as you have seen, it is usually quite unclear what the cause of the problem is from the error messages. But after quite some research, we have come up with some common reasons you might see this error show on your WordPress websites.
🔗 Incorrect Links Or URL String Syntax Error
First off, we can start with the URL syntax errors. The HTTP error 400 can occur when you or a website user is trying to access an invalid URL, which can be due to ‘illegal’ characters encoded into the URL string or ‘malformed’ link.
Note: An illegal character is one that isn’t commonly seen in URLs, while a ‘malformed’ URL appears when an extra % (percentage symbol) is inserted in the URL string.
In other cases, a website user may even send false request routing information using URL by accident. Then, to process requests securely and ensure that the user is not attempting anything illegal, certain web servers are developed to search for special HTTP headers. If an expected custom HTTP header is missing or malformed.
💻 Corrupted Browser Cache & Cookies
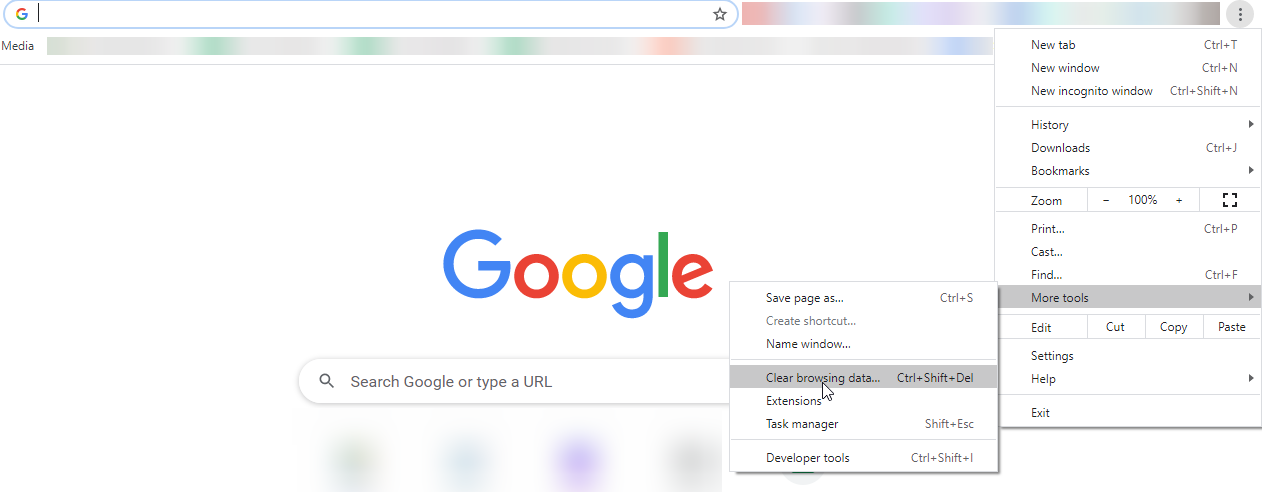
A 400 Bad Request error can also be caused by corrupted files in the browser cache or issues with expired browser cookies on your device. It is also possible that a local cookie in your web browser identifies you using a session cookie. And if this session token or cookie matches another from a different user’s request, the webserver may interpret this as a malicious action.
⚠️ Unsynchronized DNS Lookup Cache
IP Addresses of your website are stored locally in the Domain Name System (DNS) for a better user experience. However, if the DNS data stored goes out of sync with the registered ones and may be another cause of an HTTP 400 error may be that the DNS data stored locally is out of sync with registered DNS information.
This issue might arise more regularly when you are in the developing or updating process of a website, or when you are configuring your site’s domain settings.
⬆️ Incorrect File Size Uploaded To Site
Up next is the most common mistake that leads to an HTTP 400 error – uploading a file (image, video, or text content) onto your WordPress website that exceeds the size limit. This can always vary depending on how the server has been set up or what file size is considered to be acceptable.
At times like this, your web server will not be able to process the request fully and will result in a clear error code that will not let you access your web page and content.
🚫 Bad Request From Generic Server Errors
Lastly, the 400 Bad request error may be triggered because of server-side issues instead of the user-side. A common server glitch, or other unspecified temporary issues, can also lead to a bad request error message appearing on your screen.
Ways To Resolve A 400 Bad Request Error In A Few Steps
Finally, now that we know what this 400 Bad Request error is and why you might be experiencing this issue on your websites – let’s take a look at all the possible solutions you can attempt to fix this request error.
✅ Check The Requested URL For All Possible Errors

In response to the possible string syntax error of your URL, you can check the domain name of a specific page or website you are trying to access. Ensure that the browser URL is spelled and typed correctly, and there is no ‘illegal’ character.
You might opt to use an online URL encoder/decoder or a broken link checker for longer URLs to make the process much easier and less error-prone. These kinds of tools should also be able to detect illegal characters or malfunctioning URLs automatically. Afterward, if you’re still getting the 400 Bad Request error, you should move on to clearing some cache.
✅ Clear Browser Cache & Remove All Existing Cookies
If the HTTP 400 error is caused by an outdated cache of excessive cookies in your web browser, you need to clear all browsing data from your device. Moreover, clearing cache will not only help you get rid of this error but will also ensure your devices work faster and more seamlessly.

Check out our detailed blog on how to clear cache for different browsers with ease to learn in detail.
✅ Completely Clear Outdated Or Corrupted DNS Cache
Next up are DNS cache errors, and the solution to this is to clear out the data stored. You can check out this guide to learn how to flush DNS cache with ease.
Afterward, if the website loads correctly, the outdated or corrupted data has been removed from your device. But if it still persists, it’s time to check your uploaded content for errors.
✅ Ensure Uploaded File Size Does Not Exceed Server Limit
This one is quite simple. If you face this HTTP server error while trying to upload media content or file onto your website, it is quite possible that the 400 Bad Request error is a result of your file exceeding the usual size limit configured on the server.
So the solutions to this are quite simple too. First, try to upload a smaller file or a lower-resolution version of the content, and check if your website sends out the same error again. If it does not, the error was simply due to a size error and you are good to go.
✅ Deactivate Extensions, Restart Device & Contact Host
And finally, if none of the above-mentioned solutions work, it’s time to go down to the basics – deactivate extensions, restart your device, or contact your server host.
🎯 Deactivate extensions: If you have recently installed and activated browser extensions, these could actually be the culprit behind the 400 Bad Request error. Sometimes, it might even be a plugin or theme that’s interrupting your service requests. Try disabling or deactivating these tools from your browser or server to check if the web page gets back on track again.
🎯 Restarting your device: Or, try to reboot your device and related equipment. A device reboot will help to flush all stored memory and cached data, and in most cases, will ensure the 400 Bad Request error gets solved easily.
🎯 Contact your server host: If nothing works, this might be the right time to contact your hosting provider and seek their help. They might be able to inspect their server problem logs or have their own backups of your WordPress site, for example. They will surely be able to solve your problem.
Bonus: Learn To Fix HTTP Errors While Uploading Images On Your Site
And with that, we conclude our guide on how to fix a 400 Bad Request Error. To learn even more fixes to other types of HTTP errors, check out our blog here and enhance your web building and browsing experiences further than ever before. Or, check out our in-depth guide to learn about 5 common Elementor website errors
Was this blog helpful to you? Do let us know about your experiences solving this problem by commenting below. To find more blogs like this, subscribe to our blog and share your experience with us. Join our Facebook group to learn more about web design and development.








