Whether you’re running a personal blog, an e-commerce website, or a business portal, the loading speed of your web pages can make or break your online success. And when it comes to optimizing your website for speed, one metric stands out as the gold standard: the Google PageSpeed Score.
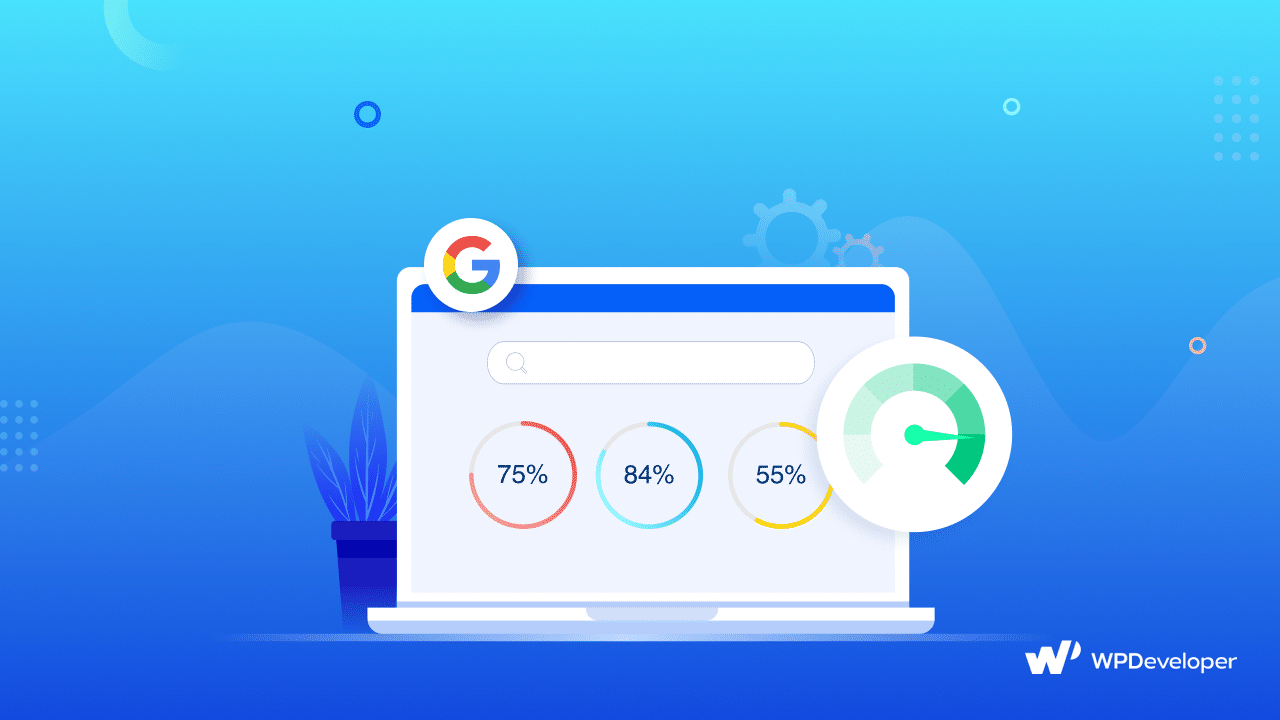
Google PageSpeed Score is not just a number; it’s a reflection of your website’s performance and user experience. It’s a critical factor that influences your search engine ranking and can significantly impact your bounce rate. In other words, a higher PageSpeed Score can lead to more visibility, increased user engagement, and, ultimately, greater success online.
What Is Google Pagespeed Score?
The Google PageSpeed Score is a numerical representation of a web page’s performance, specifically focusing on its loading speed and user experience. This score is a reflection of how quickly a page loads and how efficiently it renders content, ultimately impacting overall user satisfaction.
Search Engine Ranking: Google considers page speed as a ranking factor. Websites with faster loading times tend to rank higher in search engine results, making the PageSpeed Score critical for SEO (Search Engine Optimization).
User Experience: Slow-loading pages frustrate users, leading to higher bounce rates and decreased user engagement. A higher PageSpeed Score correlates with a better user experience, keeping visitors engaged and on your site.
Mobile Friendliness: With the increasing use of mobile devices, fast loading times are essential for catering to mobile users. A high PageSpeed Score indicates mobile-friendliness.
What Influences The Google Pagespeed Score?
Server Response Time: The time it takes for the server to respond to a request significantly impacts page speed. Optimize server response times by using efficient hosting services and content delivery networks (CDNs), and minimizing server-side processing.
Browser Caching: Caching allows browsers to store and reuse previously downloaded resources, reducing the need for repeated downloads. Properly configuring caching headers and leveraging browser caching can improve loading speed.
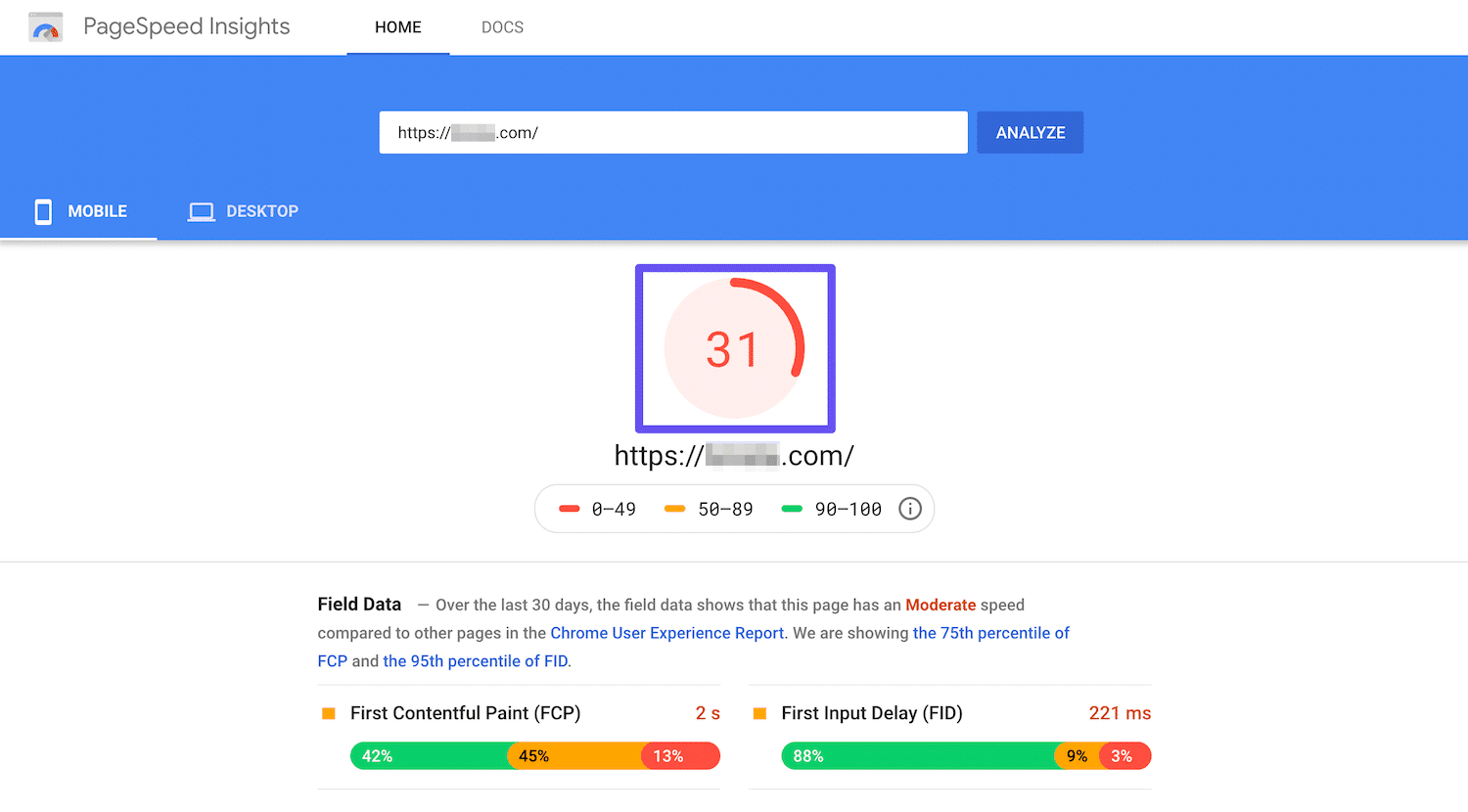
Image Optimization: Large, uncompressed images can slow down a webpage. Optimize images by using appropriate formats (e.g., WebP), resizing images to their display size, and compressing them without compromising quality.
JavaScript and CSS Minification: Minifying these resources involves removing unnecessary characters and whitespace, reducing their file size, and speeding up loading times.
Above-the-Fold Content: Prioritize loading critical above-the-fold content to provide users with a faster initial page rendering. Delay loading non-essential content until after the initial display.
7 Effective Ways to Improve Your Google PageSpeed Score
By implementing these seven strategies, you can make significant strides in improving your Google PageSpeed Score.
Optimize and Compress Images
Large, unoptimized images can significantly slow down your website. Utilize image compression tools and choose the right file format (such as WebP) to reduce image size without sacrificing quality. Also, specify image dimensions in your HTML to prevent browser reflows.
Minify CSS & JavaScript Files
Excess whitespace, comments, and unnecessary characters in your CSS and JavaScript files can bloat their size. Minify these resources to eliminate unnecessary elements, making them smaller and quicker to load.

Leverage Browser Caching
Configuring browser caching allows users’ browsers to store website assets locally, reducing the need for repeated downloads. Implement caching headers for static resources like images, stylesheets, and scripts to improve load times for returning visitors.
Enable Compression (GZIP or Brotli)
Compressing your web content using GZIP or Brotli compression algorithms can significantly reduce file sizes, leading to faster page loading. Ensure your server is configured to enable compression for text-based resources.
Prioritize Above-the-Fold Content
Deliver critical content to users as quickly as possible by prioritizing above-the-fold content. By doing this, visitors can start interacting with your page while the rest of the content continues to load in the background.
Reduce Server Requests
Minimize the number of server requests by combining and consolidating assets. Use CSS sprites for icons and consider loading third-party scripts asynchronously to prevent them from blocking page rendering.

Opt for a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Implementing a CDN can help distribute your website’s content across multiple servers located in various geographic regions. This reduces server response times and enhances loading speed for users, regardless of their location.
By implementing these seven strategies, you can make significant strides in improving your Google PageSpeed Score. Keep in mind that continuous monitoring and fine-tuning of your website’s performance are essential for maintaining a high score and providing a stellar user experience.
Accelerate Your Success With An Enhanced Google PageSpeed Score
A high PageSpeed Score brings forth a multitude of benefits. It enhances your search engine ranking, making your website more discoverable to users actively seeking your content. Moreover, it elevates the user experience, reducing bounce rates and keeping visitors engaged. In an era dominated by mobile devices, a fast-loading website is a must for catering to on-the-go users.
Don’t forget to visit our blog page for more updates, blogs, or tutorials related to WordPress and others, and join our friendly Facebook community to get attached to all WordPress experts.