Social engineering attacks are not your typical technical hacks; they involve manipulating individuals into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security. As a WordPress user or administrator, understanding and defending against these threats is crucial to safeguard your website’s integrity.
In this blog post, we will explore the world of social engineering attacks, shedding light on what they are, how they work, and most importantly, how to educate yourself and your users to ensure WordPress security.
Social Engineering Attacks: Types, Methods & Their Potent Threats
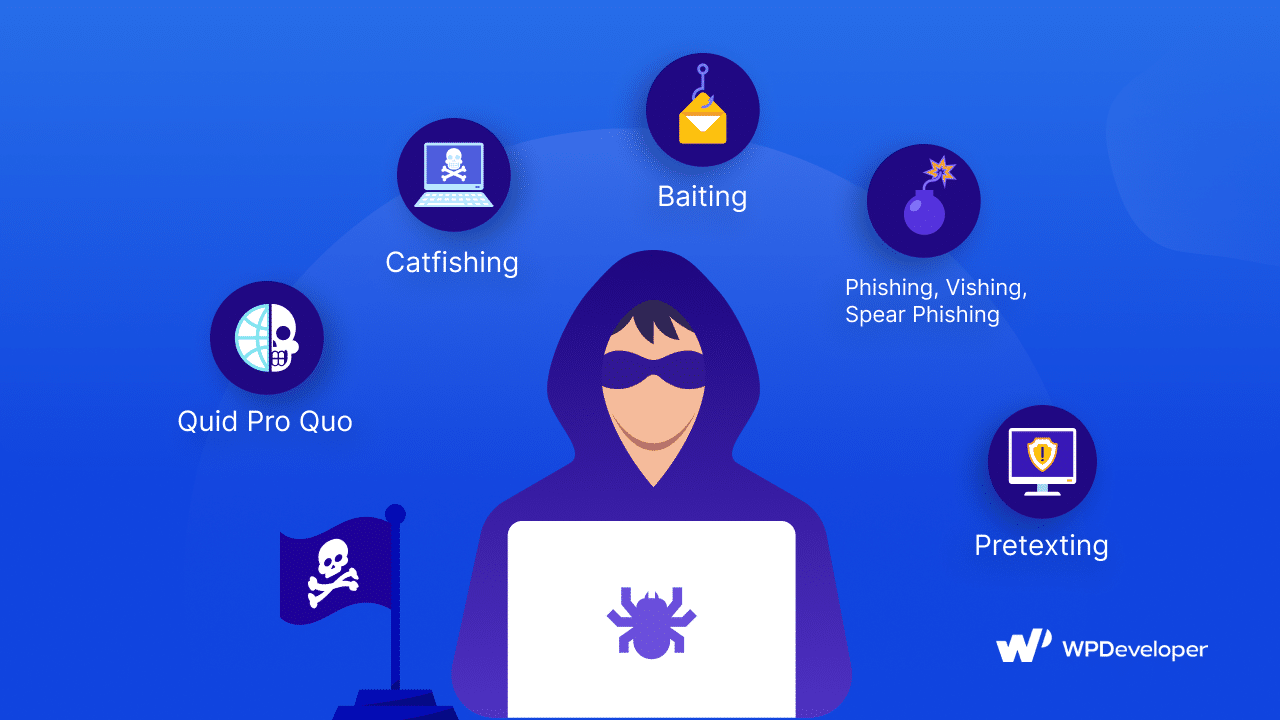
Social engineering attacks come in various forms, each designed to exploit human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities. In this section, we will delve into the diverse types of social engineering attacks, explore how they function, and assess the significant dangers they pose to the security of WordPress websites and online platforms.
Phishing Attacks: The Art Of Deception
How They Work: Phishing attacks involve the use of fraudulent emails, messages, or websites that appear legitimate to trick individuals into divulging sensitive information like usernames, passwords, or credit card details.
Danger Level: Phishing attacks are among the most common and dangerous social engineering tactics. A successful phishing attack can lead to unauthorized access to your WordPress admin panel or the compromise of user accounts.
Pretexting: Crafting Elaborate False Scenarios
How They Work: Pretexting entails creating a fabricated scenario or pretext to manipulate individuals into revealing personal or sensitive information. Attackers often pose as trustworthy entities, like customer service representatives.
Danger Level: Pretexting can lead to data breaches or identity theft, potentially causing significant damage to WordPress users and their websites.
Baiting Attacks: Temptation As A Weapon
How They Work: Baiting attacks offer enticing downloads or content, such as free software, that harbor malware. Users unknowingly download malicious files when tempted by the bait.
Danger Level: Baiting attacks can introduce malware to your website, causing harm to your site’s visitors and potentially leading to website defacement or data breaches.
Quid Pro Quo Attacks: A False Promise
How They Work: In quid pro quo attacks, cybercriminals promise a service or benefit in exchange for sensitive information. They might offer to solve an issue, like technical support, in return for access credentials.
Danger Level: These attacks can result in unauthorized access to your website, enabling attackers to manipulate content, steal data, or cause other security issues.
Tailgating Attacks: The Art Of Blending In
How They Work: Tailgating attacks involve physically following an authorized person into a restricted area or, in the digital realm, persuading individuals to provide access to restricted information or areas.
Danger Level: If your WordPress hosting environment is compromised through tailgating, it can lead to unauthorized access, data loss, or website defacement.
Understanding the various types and methods of social engineering attacks is the first step in defending your WordPress website against them.
Strengthen WordPress Security From Social Catfishing
To fortify your online presence and protect your valuable content from the ever-looming danger of social engineering attacks, it’s crucial to educate your users.
Raise Awareness
User Training: Conduct regular training sessions to make your users aware of the various social engineering tactics. Explain how these attacks work and share real-life examples to drive home the potential risks.
Security Policy: Develop a comprehensive security policy for your website, outlining best practices for users. Make it easily accessible, so users can refer to it whenever needed.
Phishing Simulations
Simulated Attacks: Consider running simulated phishing attacks on your users. These controlled exercises mimic real phishing attempts to help users recognize and report suspicious emails and messages.
Feedback And Learning: Provide immediate feedback to users who fall for simulated phishing attempts. Use this as a teaching moment to enhance their awareness and response to real threats.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA Implementation: Encourage or require users to enable multi-factor authentication or blocking IP. MFA adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
User-Friendly Options: Offer user-friendly MFA options, such as smartphone apps, text messages, or biometrics, to make it convenient for your users.

Source: University Of Manitoba
Regular Updates And Patching
System Maintenance: Stress the importance of keeping their systems and browsers up to date. Many social engineering attacks exploit outdated software vulnerabilities.
WordPress Updates: Ensure that your WordPress core, themes, and plugins are regularly updated to patch any security vulnerabilities.
Vigilance In Email And Communication
Verification: Instruct users to verify the authenticity of emails and messages before taking any action. Verify the sender’s identity, especially if a request seems suspicious.
Report Suspicious Activity: Encourage users to report any unusual or suspicious activity, whether it’s a strange email, an odd pop-up, or unexpected system behavior.
Password Management
Strong Passwords: Promote the use of strong, unique passwords. Encourage the adoption of password managers to simplify and secure their login credentials.
Password Changes: Emphasize the importance of changing passwords regularly and avoiding password reuse across multiple accounts.
Access Controls
Least Privilege: Implement the principle of least privilege, ensuring users have only the access and permissions necessary for their roles or responsibilities.
User Permissions: Review and adjust user permissions regularly to minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
Incident Response Plan
Response Training: Educate users on the steps to take in the event of a security incident. Ensure they know how to report, respond, and recover from an attack.
Testing: Periodically test your incident response plan to ensure that everyone knows their roles and responsibilities.
Nurture A Culture Of Vigilance From Social Attacks
By raising awareness, conducting simulations, and implementing multi-factor authentication, you equip your users to recognize and thwart the cunning tactics of social engineers. Regular updates, strong password management, and a well-structured incident response plan further fortify your defense. Together, these measures create a robust security culture that protects your WordPress website from the relentless threats it faces.
Don’t forget to visit our blog page for more updates, blogs, or tutorials related to WordPress and others, and join our friendly Facebook community to get attached to all WordPress experts.